Africa
From economic forecasting to in-depth coverage of city developments, and analyses of investment opportunities to the drivers impacting operational effectiveness, fuel your business growth by leveraging our complete Africa solutions.
Contact us
54
African Countries
First-hand insights on 54 African countries’ economic, political and financial market developments delivered at your fingertips.
102
African Cities
Forecasts for 102 African cities’ GDP, employment, population, household income, consumer spending and retail sales, along with city deep dive analysis.
16
Tourism Hotspots
Forecasts on passenger flows, number of overnight stays, tourism spending and more for 45 African countries and 16 major cities.
14
Key Sectors
In-depth analysis, forecasts and scenarios for 14 key industries and detailed sub-sector analysis in line with NACE revision 2 codes across 8 countries.

Africa Watchlist 2024
Next year holds promise for the dawning of a new industry in Africa and somewhat of a commercial renaissance taking place in Kenya – East Africa’s economic anchor. Our watchlist for 2024 also foregrounds major currency devaluations in Ethiopia and Egypt and a strong probability of coups d’état in Cameroon and Tunisia.
Complete solutions to fuel your business growth in Africa
Our Africa coverage provides comprehensive analysis of immediate and long-term economic prospects in addition to forecasts and commentary by country, industry sector and city.

Cut through the noise
Stay on top of the ever-evolving market and make timely calls with the support of the largest macro research team in the continent.

Informed decisions and business planning
Inform your planning with concise and action-driven insights that connect the dots among politics, economics and their implications on the market.

Manage emerging risks
Monitor and measure risks impacting investment and business environments across the continent.
Related Services

Service
Africa Forecasting Service
Comprehensive analysis of immediate and long-term economic and political prospects to inform investment strategies, expansion and African operations through forecasts and commentary by country, industry, and city.
Find Out More
Service
African and Middle Eastern Cities Forecasts
Comprehensive data and forecasts for major cities in Africa and the Middle East.
Find Out More
Service
Global Sustainability Model
Accurately measure your organisation's global footprint through economic, environmental and social lenses, identify risks and develop strategies to become more sustainable.
Find Out More
Service
City Scenarios
The depth of our data services, the expertise of our economists, our global modelling capabilities, and our technical expertise allow us to tailor data, forecasts and scenarios to your specifications.
Find Out More
Service
Industry Scenarios
Quantifying the impact of policy changes and other risk events on industrial sectors.
Find Out More
“Oxford Economics’ data and forecasts form the backbone of our demand models. The global consistency and granular detail available in their expansive dataset allows us to focus on the variables most relevant to our business.”
Resources and Events

Blog
Easter Egg-onomics
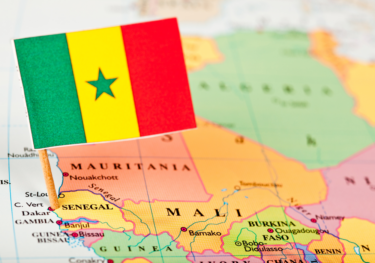
Research Briefing
Africa: Radical Faye looks strong in Senegal’s presidential election

Research Briefing
The long-term outlook for Northern African cities

Research Briefing
The long-term outlook for Middle Eastern cities

Webinar
Key elections in Africa in 2024

Webinar
Watchlist 2024 – Coups, devaluations, and the birth of a sector

Webinar
Are African countries’ fiscal efforts strong enough to restore debt sustainability?

Webinar
Pockets of value in frontier markets

Africa Watchlist 2024: Devaluations, coups, and green hydrogen
Featured
Contact us
If you would like to find out more about our services, please fill in the form and let us know a bit more about you and what you’re looking for. A member of the team will be in touch with you as soon as possible.
By submitting this form you agree to be contacted by Oxford Economics about its products and services. We will never share your details with third parties, and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Where we are in Africa
Our South Africa office’s dedicated team of economists, political analysts and sales understand the region and your needs.
Trusted By







